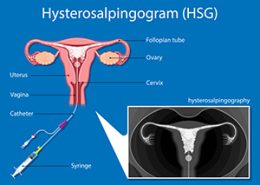
What is a laparoscopy?
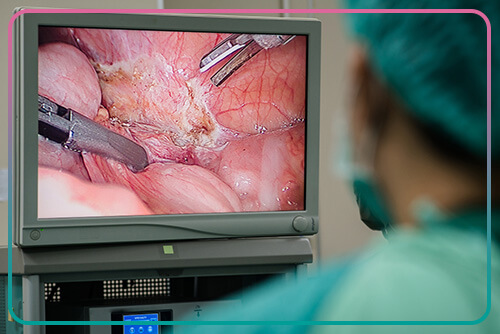
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive and low-risk surgical procedure that is used to diagnose and treat some abdominal and pelvic problems. In this surgery, one or more small incisions are made in the abdomen and a long, thin tube with a high-resolution camera and a small lamp is inserted into the body. The images of this camera are displayed to the surgeon with a monitor with appropriate magnification and resolution.
Laparoscopy is commonly used to diagnose abdominal and pelvic problems. This method is used when other non-invasive methods such as ultrasound, CT scan, and MRI cannot help with the diagnosis. In addition to diagnosis, laparoscopy is used to take samples of abdominal and pelvic tissues and perform therapeutic interventions. In this case, the surgeon may use other tools such as clamps, scissors, lasers, or electrocautery during surgery.
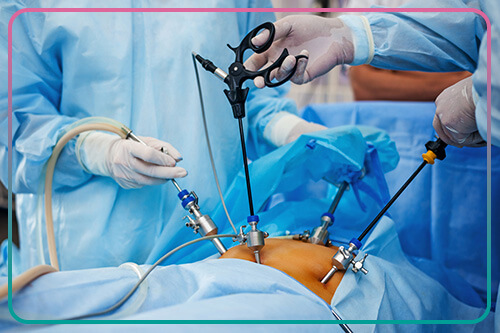
What are the applications of laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is performed with two diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. This method allows the specialist physician to identify the causes of abdominal problems and, if necessary, perform therapeutic and corrective measures. The main use of laparoscopy is to examine the abdominal organs such as the gallbladder, liver, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, spleen, stomach, and reproductive organs. Laparoscopy is used to diagnose mass or tumors of the abdomen, the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity, liver disease, the rates of cancer progression, and to evaluate the effectiveness of some treatments.
Application of laparoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility
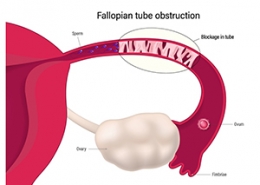
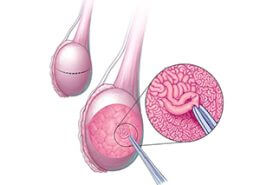
Nowadays, laparoscopy is also used to diagnose many gynecological diseases and causes of infertility. Endometriosis, uterine fibroid, adhesions, structural disorders of the reproductive system, fallopian tubes disorders, ovarian cysts, and ectopic pregnancies that cause infertility can be detected by laparoscopy. In addition to diagnosing many infertility problems, laparoscopy can also be used to treat fertility problems. Operations such as removal of endometrial tissue, adhesions, uterine fibroid, ovarian cysts, and the opening of fallopian tubes, and in some cases removal of the uterus or closing of fallopian tubes can be performed by laparoscopy.
How is laparoscopy performed?
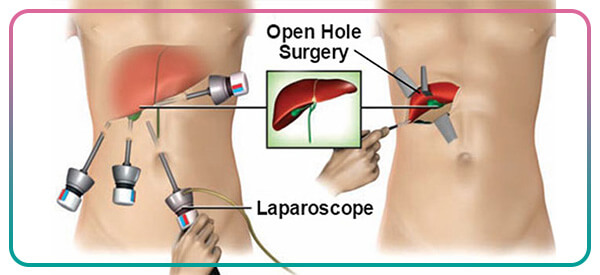
Laparoscopy is an outpatient surgery performed under general anesthesia. In this procedure, the surgeon first inserts some carbon dioxide gas into the abdomen using a special needle. This gas creates enough space under the abdominal wall and makes it easier to see the organs by pushing back the intestines. The surgeon then makes a small incision under the umbilicus and inserts a laparoscope into the abdomen. A laparoscope is a long, narrow tube with a small camera at its head that sends high-quality images of the abdominal cavity to a monitor. By making a second incision, the doctor inserts another instrument into the abdomen to move the organs inside the abdomen and examine the surrounding area.
If laparoscopy is performed for a biopsy (sampling) or treatment, the surgeon makes one or two more incisions in the lower abdomen to insert special surgical instruments into the abdomen. During the biopsy, a small sample of the tissue is taken and sent to a laboratory for testing. After surgery, the abdomen is emptied of carbon dioxide and the instruments are removed. Finally, incisions in the abdomen are closed with sutures or surgical tape.
How to get ready for a laparoscopy?
The necessary preparations before performing a laparoscopy are:
1- It is necessary to avoid eating and drinking for at least 8 hours before surgery.
2- Before having a laparoscopy, your doctor may order doing blood and urine tests, electrocardiograms, ultrasounds, or CT scans. These tests help your doctor better diagnose problems during a laparoscopy. In addition to the imaging results, it provides a physician with a visual guide from inside the abdomen.
3- The doctor should be aware of any medications that the patient is taking. You should also inform your doctor if you are pregnant or even suspect you may be pregnant. Because your doctor may need to change the dose of anticoagulants, anti-inflammatory drugs, dietary supplements, and vitamin K, which can affect the laparoscopic result.
What are the benefits of having a laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is a low-risk and almost safe surgery that has several advantages. Repairing and treating abdominal problems during diagnostic surgery is one of the most important benefits of laparoscopy. So that, the surgeon during the operation can diagnose the lesion and the problem and repair it with other tools.
Laparoscopy has a shorter recovery period than open surgeries and allows a person to return to daily activities more quickly. Laparoscopy is also performed without the intervention of the hand and by magnifying the camera and delicate instruments. Therefore, the operation is more precise and delicate than open surgery, and the amount of adhesions, infection, and pain after the operation is much less.
Laparoscopy can help treat many causes of infertility in women, such as closed fallopian tubes, endometriosis, ovarian cysts, etc. Some women get pregnant naturally by having a laparoscopy and removing barriers to fertility. In some women, laparoscopy is also used to treat uterine problems before infertility treatments such as IVF, ICSI, or donated eggs.
What are the complications of laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is a low-risk surgical procedure and is rarely associated with complications. The most common laparoscopic complication is shoulder and neck pain. This pain is due to the accumulation of carbon dioxide gas, which is used to inflate the abdomen. This gas can irritate the diaphragm and cause nerve sensation and pain in the shoulders and neck. This pain and discomfort can last up to 2 days.
Laparoscopy should be performed by a qualified and experienced physician. If laparoscopy is not done carefully enough, it can cause bleeding, infection, or damage to the abdominal organs. The patient should be on the lookout for signs of infection after surgery, such as:
- Fever and chills
- Abdominal pain that gets worse over time
- Redness, swelling, and bleeding or discharge of fluid at the incision site
- Nausea
- Shortness of breath
- Inability to urinate
- Headache
Laparoscopy may be associated with complications of general anesthesia, including hoarseness and sore throat, nausea, dizziness, and itching. These side effects are short-lived and resolve within a day. If laparoscopic complications do not resolve within a short time or worsen over time; you must see a specialist.
What care should be taken after laparoscopy?
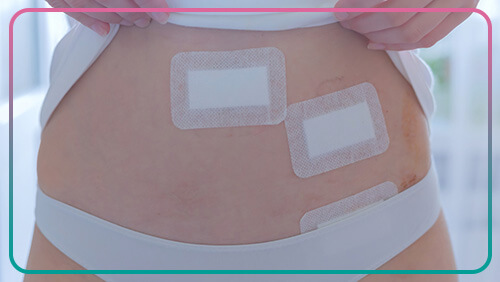
One of the most important cares after laparoscopy is to keep the surgical incision clean and dry. This care reduces the risk of infection. Your doctor may prescribe painkillers to relieve minor pain from surgery. If the pain does not go away after a few days, you must inform your doctor. It is better to wear loose clothes after laparoscopy and rest more time. Up to one week after laparoscopy; Exercise and lifting heavy objects should be avoided. In order to prevent blood clots, it is recommended to do light activities in the first days after laparoscopy. Nausea is normal due to anesthesia during surgery. To improve this condition, it is better to eat light foods two days after the operation. It is necessary to see a doctor at the appointed time in order to perform postoperative examinations to ensure the correct recovery process.
Laparoscopy in Iran
Laparoscopic surgery services are provided in the best infertility treatment centers in Iran in order to diagnose and treat the causes of infertility. Laparoscopy in Iran is performed using up-to-date instruments and by specialized and skilled Iranian physicians with great precision and delicacy. Couples from many parts of the world for laparoscopy; Diagnosis of causes and treatment of infertility travel to Iran. The cost of laparoscopy in Iran is between $ 1,000 and $ 2,000. For more information about laparoscopy in Iran and to get advice from specialist doctors, you can contact us.