Recurrent miscarriage: Causes and treatment
Miscarriage is an unpleasant event that may occur to many couples. Fetus loss can negatively affect the mental health of couples, particularly in the case of recurrent miscarriages. Many couples are discouraged and disappointed with the first miscarriage. Yet, the good news is that many couples experience miscarriage only once and have no problem with childbearing. Nearly 1-2% of women experience recurrent miscarriages, requiring a specialist examination for the necessary therapeutic measures.
It is recommended to perform necessary tests after the second consecutive miscarriage to determine its cause. Approximately 60% of recurrent miscarriages occur due to fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Moreover, the increased maternal age reduces the quality of the ovum and increases genetic abnormalities, thus increasing the risk of recurrent miscarriage. Hormonal disturbances, immune system, and some underlying diseases such as diabetes, thyroid disorder, hypertension, and poor sperm quality are other reasons for recurrent miscarriage. Many couples with recurrent miscarriages can successfully terminate their pregnancies with timely treatment.

What is recurrent miscarriage?
According to the American Society of Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), Recurrent miscarriage is defined as a minimum of two consecutive miscarriages, i.e., fetal death before development and reaching the end of the pregnancy, usually occurring in the first 5 months of pregnancy before the 20th week. The first time of miscarriage is very common and is not usually repeated, thus not requiring medical attention. Though, in case of repeated miscarriage for the second time, both men and women should undergo medical examinations.
The probability of repeated miscarriage is nearly 24% after the first miscarriage, 30%after two consecutive miscarriages, 35% after three consecutive miscarriages, and 40% after 4 consecutive miscarriages. Thus, performing the necessary medical tests and investigations to investigate the cause of recurrent miscarriage after the second successive miscarriage is vital.
What are the common causes of recurrent miscarriage?
Several factors affect the recurrent miscarriage fertility issue. The reason is identified in half of the cases after initial medical tests and investigations. However, the cause of approximately half of recurrent miscarriages is not found. The following items are the most common causes of recurrent miscarriage:
-
Fetal genetic abnormalities
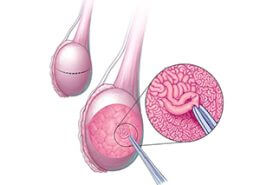
Recurrent miscarriages most commonly occur due to chromosomal abnormalities. The healthy cells have 46 chromosomes containing growth genes. If the embryonal cells have fewer or more chromosomes, chromosomal abnormalities usually do not allow the fetus to grow and cause miscarriage.
Fetus chromosomal abnormalities are usually caused by miosis division problems in the formation of the ovum. Thus, the low quality of the ovum highly affects the incidence of fetus chromosomal abnormalities. With increased maternal age, the ovum quality is decreased, which increases the risk of fetal abnormalities and miscarriage. Thus, it is recommended that women plan to get pregnant before the age of 35.
In addition to the quality of the ovum, poor sperm quality, such as chromosomal abnormalities and fragmented DNA, can cause genetic problems in the fetus and increase the risk of miscarriage. Sometimes, the quality of the ovum and sperm is good, yet, parents have minor genetic abnormalities that aggravate the fetus and result in miscarriage.
-
Uterine structural problems
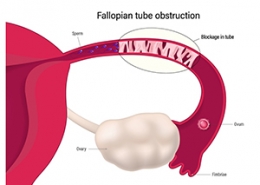
Uterine structural abnormalities are among the most common causes of recurrent miscarriage and include uterine septum, myomas, polyps, fibroids, uterine adhesion, and cervical insufficiency, playing significant roles in recurrent miscarriages. Usually, these abnormalities lead to miscarriage in the second trimester of pregnancy.
-
Hormonal disturbances
Hormonal disturbances, including thyroid dysfunction and polycystic ovary syndrome, can cause miscarriage before week 10 of pregnancy. Fetal growth during the first 2 months of pregnancy highly depends on the level of progesterone hormone produced by the ovaries. In the case of progesterone deficiency, fetal growth is stopped, leading to miscarriage. Hypothyroidism is among the causes of ovarian dysfunction causing miscarriage.
Moreover, increased level of blood male hormones and insulin in women with polycystic ovary syndrome causes inappropriate hormonal conditions in the uterus and increases the risk of miscarriage.
-
Disruption of the mother’s immune system
The fetus needs a suitable and safe environment for implantation in the uterus, and the disorders of the mother’s immune system can cause miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy. Anti-phospholipid syndrome is one of the most common immunological causes of recurrent miscarriage, in which antibodies made by the mother’s immune system cause abnormal blood coagulation, and the fetus’s blood supply is disrupted, eventually leading to miscarriage.
-
Underlying diseases
Diabetes, blood coagulation disorders, and several parasitic and infectious diseases increase the risk of recurrent miscarriage. Therefore, mothers with these underlying diseases should be supervised by a doctor before and during pregnancy for disease control and to reduce the risk to the fetus.
-
Inappropriate lifestyle
Smoking, tobacco use, high caffeine consumption, and maternal obesity increase the recurrent miscarriage risk. Moreover, environmental toxins exposure, including the lead in polluted air, operating room anesthesia gases, and fertilizers, may lead to miscarriage.

How is the cause of recurrent miscarriage diagnosed?
In order to identify the causes of recurrent miscarriage, the specialist first takes a complete history of surgeries, genetic disorders in the family, etc. Then, the uterus abnormalities are examined. Finally, it is tried to identify the main causes of recurrent miscarriage based on the following tests:
-
Karyotype test
The karyotype test is used to determine the chromosomal makeup of the individuals in both males and females. It aims to find the parents’ genetic abnormalities which may be inherited by their children and cause miscarriage.
-
Evaluation of uterine cavity
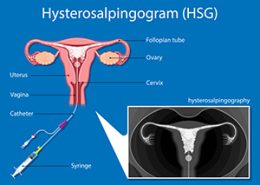
Several methods may be used to evaluate the uterine structure, including trans vaginal ultrasound, hysterosalpingography, hysteroscopy, MRI, etc. These methods are used to assess the uterus and fallopian tubes to identify uterine abnormalities which may lead to miscarriages.
-
Hormonal tests
Blood tests can measure the mother’s hormone levels, determining the levels of thyroid hormones, prolactin, androgens, blood sugar levels, and hemoglobin.
-
Infection assessment
Evaluation of vaginal discharge and measurement of maternal blood antibodies is one of the steps to assess the cause of recurrent miscarriage.
-
Evaluation of immune system
At this stage, the level of antibodies affecting recurrent miscarriage, particularly antiphospholipid antibodies, is evaluated.

-
Ovarian reserve test
An ovarian reserve test is done to assess ovulation and find possible causes of ovarian dysfunction, which may lead to fetal chromosomal abnormalities and increase the risk of miscarriage.
-
Sperm quality test
Sperm analysis and DFI tests are used to evaluate sperm quality; abnormal sperm morphology and sperm DNA fragmentation can be the reasons for miscarriage.
Treatment of recurrent miscarriage
After careful examinations and consideration of the test results, the specialist attempts to determine the cause of recurrent miscarriage. The treatment process begins with identifying the cause of the recurrent miscarriage. These treatment choices include:
-
Recurrent miscarriage due to genetic disorders
If genetic disorders are diagnosed in the study of parental karyotype, the best treatment for preventing recurrent miscarriage is to perform IVF with PGD. In this method, the parents’ eggs and sperm are fertilized together in the test environment, and embryos are formed. In the next step, embryos are genetically examined, and healthy embryos are chosen for transfer to the mother’s uterus; if all embryos are genetically impaired, the use of donated ovum or donated embryos is recommended.
-
Recurrent miscarriage due to uterine abnormalities
If structural disorders of the uterus cause recurrent miscarriages, laparoscopic surgeries and hysteroscopic surgeries are recommended to reduce the risk of miscarriage by modification of the uterus structure.
If the miscarriages occur due to cervical failure, it is suggested to perform cervical cerclage at the gestational weeks 12-14.
-
Recurrent miscarriage with hormonal causes
In miscarriages with hormonal causes, it is recommended to use intravenous progesterone or progesterone in the suppository form if the progesterone level is low.
If thyroid problems cause miscarriage, thyroid hormone levels should be controlled by medication before pregnancy.
Special medications should be used to control the prolactin level in patients with high prolactin levels.
If the level of androgen hormones is high in the mother’s blood, the specialist prescribes oral contraceptives before pregnancy to reduce the level of androgen hormones. After ensuring the reduced androgen hormones in the blood, the contraceptive pills are discontinued to get pregnant.

-
Recurrent miscarriage due to immune system disorders
In cases of recurrent miscarriage due to immune system disorders, a specialist may prescribe immunosuppressive agents, usually until the 20th week of pregnancy.
-
Recurrent miscarriage due to coagulation problems
In case of coagulation disorders, taking aspirin, vitamin D, and folic acid for at least 2 months before pregnancy is recommended.
In some cases, it is recommended to take injectable anticoagulants such as heparin and enoxaparin at the beginning of pregnancy usually lasts until the 20th week of pregnancy.
-
Recurrent miscarriage due to high blood sugar
If blood sugar levels cause recurrent miscarriage and hemoglobin A1C is high, the specialist will carefully control blood sugar and hemoglobin A1C levels. Pregnancy may occur after ensuring a normal blood sugar level and hemoglobin A1C state.
-
Improving lifestyle
Lifestyle is among the factors affecting recurrent miscarriage. Weight loss, proper nutrition, regular exercise, smoking cessation, limiting caffeine use, and avoiding stress can remarkably prevent miscarriage.

Conclusion Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: Diagnosis, and Therapy
Fortunately, most couples successfully terminate pregnancies, though nearly 2% of couples suffer two or more recurrent miscarriages. Couples with recurrent miscarriages need to visit a specialist for the causes of the miscarriage. After examinations and laboratory tests, the causes of recurrent miscarriage may be identified in nearly 50% of the cases. In cases of identifying the cause of recurrent miscarriage, the patient may receive medication, undergo surgeries, or use assisted reproduction techniques such as IVF, ICSI, and PGD, either with the use of a donated ovum or fetus for the treatment of recurrent miscarriage.