Can you get pregnant with blocked fallopian tubes?
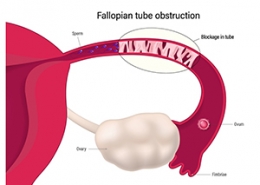
Damaged or blocked fallopian tubes are among women’s most common causes of infertility. These tubes are part of the reproductive organs of women and play an important role in the reproductive process. Obstruction of the fallopian tubes can prevent the sperm from reaching the egg or prevent the movement of the fertilized egg toward the uterus. The blockage or damage to these tubes may be caused by pelvic inflammatory diseases, endometriosis, previous surgeries, ectopic pregnancy, etc. In some cases, one of the fallopian tubes may be blocked, so there is still the possibility of pregnancy with a healthy tube. If the damage or bilateral blockage of the fallopian tubes cannot be resolved through medical procedures, there is still the possibility of pregnancy using in vitro fertilization methods such as IVF and ICSI.
How do damaged fallopian tubes cause infertility?
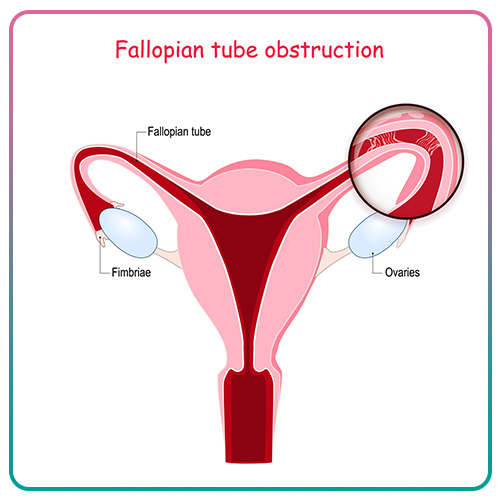
About 30% of women suffering from infertility face problems of obstruction or damage to the uterine tubes. The fallopian tubes are one of the organs of the female reproductive system that connect the ovaries and the uterus. During ovulation, the eggs are released from the ovaries and move through the fallopian tubes to the uterus. Sperms also enter the fallopian tubes through the vagina. Sperm and egg fertilize each other in the middle of the fallopian tube. The fertilized egg must pass through the fallopian tube and enter the uterus for pregnancy to occur. In case of damage or blockage of the uterine tubes, the movement of the sperm toward the egg or the movement of the fertilized egg toward the uterus will be disrupted. Therefore, the health of the fallopian tubes plays an important role in the fertility process.
What is the cause of blocked fallopian tubes?
Fallopian tubes are easily damaged due to their small size. These tubes are usually blocked by scar tissue or adhesions and pelvic infections. Scars and infections in uterine tubes can be caused by many factors, the most common of which are:
-
Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases (PID)
Sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia and other infections can lead to pelvic inflammatory diseases if left untreated. These infections cause sores and inflammation near the fallopian tubes and block them. Therefore, inflammation and infection of the cervix should be taken seriously and treated so that it does not lead to obstruction of the uterine tubes.
-
Endometriosis
It means the growth of the inner tissue of the uterus, outside the uterus, which can involve the pelvis, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Endometriosis that develops on or near the fallopian tubes can cause adhesions, scarring, or blockage of the tubes. Learn more about Endometriosis and fertility: Endometriosis and infertility
-
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tubes instead of the uterus. Since the fallopian tubes are very narrow, the fertilized egg does not have enough space to grow, which can cause a rupture of the tubes and be dangerous for the mother. In case of timely diagnosis by the doctor, the fertilized egg can be removed by surgery. But surgery can scar the tubes and sometimes remove them.
-
Fibroid
They are benign pelvic tumors that grow in the muscle layers of the uterus. Overgrowth of fibroid may block the fallopian tubes.
-
History of abdominal surgery
Past surgeries in the pelvic area can cause scarring and adhesions and damage the uterine tubes.
-
Tubectomy
It is an elective surgery where a person decides to block the end of their fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of blocked fallopian tubes?
Damage or blockage of the fallopian tubes usually does not have any specific symptoms. Infertility or difficulty conceiving may be the first symptom that informs women of damage or blockage of the fallopian tubes. In a type of fallopian tube blockage called hydrosalpinx, you may experience mild, regular pain in your pelvis or abdomen. Hydrosalpinx is a type of blockage of the fallopian tubes where the tubes become filled with fluid and become swollen. Although blockage of the fallopian tubes often has no symptoms, factors that can lead to damage or blockage of the tubes cause their own symptoms. For example, endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease may cause painful periods, pain during intercourse, or heavy bleeding during or between periods.
How is obstruction of the fallopian tubes diagnosed?
-
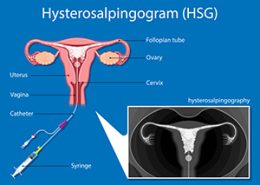
Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
The best method to detect blockage of the fallopian tubes is hysterosalpingography (Hysterosalpingogram). In this method, the doctor injects a safe-colored solution through the vagina into the uterus. This colored substance is visible in the X-ray image by creating visual contrast. If the fallopian tubes are blocked, the dye does not enter the tubes and can be seen in the photo. The best time to do a color photo is one week after the menstrual cycle and before ovulation. It is necessary to ensure the absence of pregnancy before taking a color photo.
-
Sonohysterography
It is very similar to a color image of the uterus. In this method, the saline serum is used instead of dye, and sound waves are used instead of X-rays to take pictures of the uterine tubes.
-
Laparoscopy
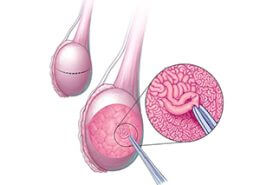
In some cases, the doctor uses the laparoscopy method to diagnose uterine tube blockage for a more detailed examination. In this procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision on the abdomen and inserts a small camera into the body to observe the condition of the fallopian tubes. Although laparoscopy is the most accurate method for diagnosing uterine tube obstruction, it is not used as the first method to diagnose uterine tube obstruction due to its invasive nature.
How are the blocked fallopian tubes treated?
The treatment method for a blocked fallopian tube can be different depending on the amount and location of the blockage. In cases where the blocked uterine tubes are small, the injection of a dye in the process of the color image of the uterus can help to remove the blocked fallopian tubes. But in most cases, surgery is the main option for treating blocked fallopian tubes. Some of the methods of treating blocked fallopian tubes include:
-
Hydrosalpinx surgery (salpingostomy)
This procedure is usually used when the blockage of the fallopian tubes causes swelling and accumulation of fluid in the tubes. In a salpingostomy, the doctor separates the damaged parts of the tube and reconnects the two healthy parts. Among the complications of this surgery, we can mention the growth of new scar tissue in the fallopian tube and the increased possibility of ectopic pregnancy.
-
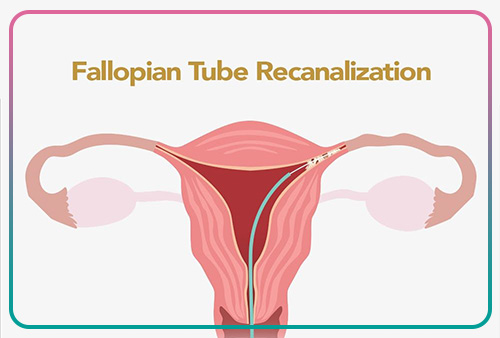
Tubal cannulation
It is a non-surgical method to treat the uterine-blocked tube. This method is usually used when the obstruction is at the end of the tube and near the uterus. In this method, the doctor, under ultrasound guidance, inserts a special catheter through the vagina into the uterus and uterine tubes. Ultrasound helps the doctor find the exact location of the obstruction. After identifying the location of the blockage, the doctor can remove the blockage by inflating a small balloon or passing a thin wire. Tubal cannulation is one of the low-risk methods of treating uterine tube blockage. But it should be noted that the doctor’s lack of experience can increase the possibility of infection or rupture of the wall of the fallopian tube.
-
Laparoscopy
If the fallopian tubes are blocked due to small adhesions in the pelvic space, laparoscopy is used to remove the adhesions and open the fallopian tubes. Of course, this method is not effective in situations where there are numerous thick adhesions.
Pregnancy after the treatment of fallopian tube obstruction
If one of the fallopian tubes is blocked, it is still possible to get pregnant naturally with a healthy tube. But if both tubes are damaged, the obstruction must be removed for normal pregnancy. The probability of pregnancy after treatment depends on the age of the woman, the length of the fallopian tubes, the severity and location of the injury, and the quality of the husband’s sperm.
A successful pregnancy occurs more often when the blocked fallopian tubes are near the uterus. If the obstruction is near the ovaries, the success rate of the treatment will be reduced. The pregnancy chance after surgery for damaged tubes due to infection or ectopic pregnancy is very low and depends on the location and amount of tube to be removed.

If pregnancy does not occur after opening the fallopian tubes, the doctor recommends IVF. IVF increases the chances of pregnancy in people who have problems with blocked fallopian tubes. In this method, the doctor stimulates the ovaries by prescribing hormonal medicine to release more eggs. When the eggs are ready for fertilization, the doctor picks up them from the ovaries during a short operation. The eggs are fertilized with the spouse’s sperm in the laboratory environment and an embryo is formed. Usually, one or two embryos are transferred to the mother’s uterus and the remaining embryos are frozen. Learn more about frozen embryo transfer (FET): Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) Procedure
Do the fallopian tubes have to be open for IVF?
In the IVF method, the eggs are removed from the ovaries using a special tool, and fertilization is done outside the mother’s body. Therefore, there is no need to open the fallopian tubes to perform IVF. But checking the health of uterine tubes before doing IVF is very important. If the fallopian tubes are blocked and swollen due to reasons such as infection, ectopic pregnancy, etc., liquid usually collects at the place of obstruction. This liquid and secretions can leak into the uterus and endanger the health of the fetus. Therefore, doctors recommend that before embryo transfer in the IVF process, a color image of the uterus should be done to check the uterine tubes for inflammation and swelling. If there is swelling in the uterine tubes, these tubes should be closed at the junction with the uterus by laparoscopy. This can help the health of the fetus and increase the chances of pregnancy.